The Effects Of Covid-19 On The Financial Performance Of Insurance Companies: A Cross Country Analysis Of ROA, ROE And Stock Returns
Research Proposal
This study aims to understand the impact that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on the profitability of insurance firms around the world during 2020 and 2021. The research uses the regression analysis method to analyze the annual number of COVID-19 cases and the profitability of insurance companies based on ROA, ROE, and Stock Return. A sample of fifty insurance companies with total assets valued above $50 million and from five continents have been selected using cluster sampling methods. The research question that is being assessed is to what extent has the COVID-19 pandemic affected the profitability of insurance firms.
Keywords: Covid-19, Insurance Firms, Profitability
INTRODUCTION
The interest in the monitoring and control of infectious diseases and the importance of these as an economic development issue has been renewed over recent years. The outbreak of infectious diseases can exact a high human and economic cost through illness and death. Disease outbreaks can cause severe economic disruptions even when there is little illness or death, according to a study by (Brahmbhatt & Dutta, 2008), as seen in cases such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in East Asia in 2003 or the plague in India in 1994. Such disruptions are the result of panicked individuals trying to avoid becoming infected. Throughout history majority of outbreaks of diseases have had a short-lived economic and financial effect but there have also been cases in which an outbreak has completely devastated the world both through death and economic development, such as the case of the 1918-1919 Spanish flu pandemic one of the deadliest epidemics in recent history which is estimated to have infected 500 million people around the world and caused 30 to 50 million deaths. According to research by Global Financial Data, Taylor (2020) the stock market’s response to Spanish influenza in 1919 is interesting to contrast with the coronavirus in 2020. In 2020 the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped over 2,000 points in four days out of fear of continued coronavirus spreading disrupting supply chains and influencing the world economy. However, the Dow Jones average at the height of the first wave of the Spanish flu pandemic was relatively unaffected. Insurers are important financial intermediaries, with almost 20 trillion dollars in assets throughout North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific and more than 33 trillion dollars worldwide (FSB 2021). COVID-19 will have a direct and indirect impact on insurers, directly via health shocks such as increased mortality and morbidity, and indirectly through financial stocks such as widespread shareholder equity losses. Insurance companies in general play a critical role in ensuring the overall economic and financial stability of a country (Karim & Jhantasana, 2005), as a result, this study aims to look at the profitability of the insurance sector by measuring the return of assets (ROA), Return of Equity (ROE), and Stock Return of various countries around the world. Based on this measure we can determine the overall financial standing of the insurance sector during the two years of the pandemic.
STATEMENT OF PURPOSE
This study aims to understand the financial performance of insurance firms during the Covid-19 pandemic and to what extent has the pandemic affected the profitability of Insurance Firms?
LITERATURE REVIEW
According to a study done on the impact of the covid 19 pandemic and the return of insurance firms by Farooq, Nasir, Bilal, and Quddoos (2021), Insurance companies across various countries such as Canada, the USA, the UK, India, and Indonesia have had an abnormally high return during the year of 2020. The study also found that the systemic risk affecting the firms, the size of the firms, and the dividend payout policy had a significant impact on those high returns. In similar research, Nayak, and Bhattacharyya, (2021) address managers’ struggle during the chaos and complexity surrounding the COVID-19 outbreak, highlighting the fundamental shift in health insurance organizations’ strategic orientation.
A study on the insurance market of China conducted by Wang, Zhang, X. Wang, Fu, (2020) reveals that. The commercial insurance premium income, the depth of insurance, the insurance density, the and monthly yearly premium growth rate all decreased due to Covid-19. Both statistically significant are the negative impacts on property and personal insurance. Increasing the level of social security and digital insurance can help to alleviate the pandemic’s detrimental effects. Babuna, Yang, Gyilbag, Awudi, Bian, (2020) carried out a study on the impact of the pandemic on Ghanaian insurance firms from March to June 2020 with a comparison to the previous pandemics such as Spanish flu and H1N1, and the result showed there is a trend of economic recession with a decline in profit by 16.6%, increase in premiums by 17.01% and increase in claims by 38.4% within the period under review. The research also indicated the Ghanaian insurance market will continue to be negatively affected during the year while eventually bouncing back in 2021.
Another study conducted by Kirti, and Shin, (2020) stated life insurers can be very heavily affected. If mortality reaches levels observed in major pandemics like the Spanish flu, payouts for life insurers would be considerable in proportion to capital. The tough climate would be compounded by widespread asset rates and persistently low-interest rates. Regulators must closely monitor and re-evaluate links to rating actions within supervision frameworks and enhance the supervision for hazardous holdings insurers in an environment that involves extensive downgrades in the bond rate. Any adjustments would nonetheless have to be carefully crafted to prevent the lowering of capital requirements overall.
CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF THE STUDY
Based on the provided literature and the problem statement a conceptual model has been illustrated in Figure 1. The conceptual model entails the hypothesis developed by analyzing the impact of Covid-19 on profitability measures such ROA, ROE, and Stock Return while also controlling other factors such as Interest rate risk, Market Risk, and Catastrophe Hazard Risk.
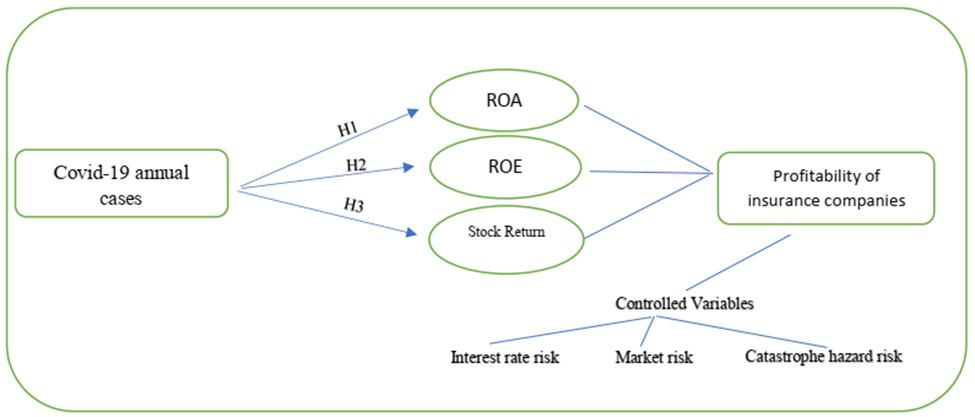
Figure 1. Conceptual Model of The Impact of The Covid-19 on Profitability of Insurance Firms
According to the relevant literature and discussions in this proposal, this study proposes the following hypothesis
H1: There is a negative link between the Return on Assets (ROA) of Insurance Companies and the number of Covid-19 cases/ deaths
H2: There is a negative link between the Return on Equity (ROE) of Insurance Companies and the number of Covid-19 cases/ deaths
H3: There is a negative link between the stock return of insurance companies and the number of Covid-19 cases/ deaths
METHODOLOGY
The research approach used in the study is a causal relationship between the independent variable which is Covid-19 and the dependent variable profitability. The study follows a regression analysis method developed on previous studies on covid-19 and stock prices such as Herwany, Febrian, Anwar, Gunardi (2021) et.al.
METHOD
People
The population in the study will consist of 50 publicly-traded insurance companies with total assets surpassing $50 million from Africa, Asia, Europe, North and South America. To avoid bias and misrepresenting, it is very crucial that the data represents all the five continents, as a result, data will include a cluster sampling method that is first employed to represent five continents from which ten samples for every continent will be taken. Then 10 of the Publicly traded insurance firms will be chosen from each continent using a random sampling method.
Measures
Based on the relevant literature and discussion proposed in this proposal, a regression analysis, Ordinary Least Square (OLS) method will be used, to assess the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on Profitability. Profitability in this case is measured in two ways. First, the financial statements such as balance sheets and income statements of publicly traded companies will be used to determine the profitability ratios, ROA and ROE. Second, the market value of the stocks will be also be used to measure the profitability of those companies during the pandemic. While the Number of Covid-19 cases will be annualized and taken from an online data base “Worldometer”.
Procedure
To answer the stated research questions, a causal research method will be employed. The time period that will be used in this study is 2 years. The research will be on an annual basis so it is divided into two time periods 2020 and 2021. First, we will look at the impact of the pandemic for 2020 and then for 2021. The number of covid cases will be annualized and taken from an online database. The study looks at the impact of the pandemic on profitability from three dimensions, as a result, three different regression models have been developed.
According to H1, there is a negative connection between financial performance measured by ROA and the number of covid cases/deaths reported annually, as a result, the first regression model equation that is proposed in this study is,
ROAt=β0+β1C+ϵt (1)
Where ROAt is the return on the asset during the period t, C is the number of covid cases/ deaths in the period t. Return on assets (ROA) is net income after taxes to total assets that illustrates how productive a company’s assets are at generating profit (Fridson, M. S. & Alvarez, F. 2011). Since most publicly traded companies release financial statements quarterly, the financial statements will be annualized by adding the values found in the financial statements the balance sheet, and the income statement at the beginning of the year to the values at the end of the year. The ROA will also be modified to represent the average of 50 companies.
According to H2, there is a negative connection between financial performance measured by Return of equity (ROE) and the number of covid cases reported annually. as a result, the second regression model equation that is proposed in this study is,
ROEt=β0+β1C+ϵt (2)
Where ROEt is the return on equity during the period t, C is the number of covid cases/ deaths in the period t. Return on equity (ROE) is a proportion of net income after tax to total equity, Because the purpose is to benefit shareholders, ROE is the genuine bottom-line measure of performance in an accounting sense (Essentials of Corporate Finance, Ross, Westerfield, Jordan, 2017). ROE will also be the average of the population sample of 50 companies.
According to H3, there is a negative connection between financial performance measured by stock returns and the number of covid cases reported annually as a result, the third regression model equation that is proposed in this study is,
SRt=β0+β1C+ϵt (3)
Where SRt is the stock return during the period t, C is the number of covid cases/ deaths in the period t. Stock return measures the return on a stock investment by calculating the appreciation or depreciation in the price of the stock plus any dividend paid divided by the initial price of the stock (Essentials of Investment, Bodie, Kane, Marcus, 2017). The average appreciation or depreciation of stock return for 50 companies will be used in this model.
Analytical plans
“EViews” will be used to assess the annual covid-19 cases and the profitability measures of ROA, ROE, and stock return. Based on our regression models the program will test for a causal relationship between the annual covid 19 cases and profitability and a summary of Statistical averages will be produced. Moreover, the regression analysis will help us compare the profitability during the period 2020 and 2021.
CONCLUSION
Despite various studies on the impact of Covid-19 and the financial performance of insurance firms, a majority of the studies focuses on the impact of the pandemic on life insurers and the structural changes of insurance firms due to the pandemic this indicates that there is scarce information on the profitability of insurance firms during the pandemic. The whole Financial sector is among the most heavily affected sectors by the pandemic. I believe this research can provide an overview on the financial performance of insurance firms during this period and help Insurance firm asses their policies during major systemic risks such as the pandemic.
REFERENCES
Herwany, Febrian, Anwar, Gunardi /Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business Vol 8 No 3 (2021) 0039–0047 doi: 10.13106/jafeb.2021.vol8.no3.0039
Babuna, P.; Yang, X.; Gyilbag, A.; Awudi, D.A.; Ngmenbelle, D.; Bian, D. The Impact of COVID-19 on the Insurance Industry. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165766*
Bodie, Kane, Marcus, (2017). Essentials of Investment, 10th edition, McGraw-Hill Education
Brahmbhatt & Dutta, (2008). On SARS Type Economic Effects during Infectious Disease Outbreaks. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/6440*
Fridson, M. S. & Alvarez, F. (2011). Financial statement analysis: a practitioner’s guide. John Wiley & Sons.
Karim, M. Z., & Jhantasana, C. (2005). Cost efficiency and profitability in Thailand’s life insurance industry: a stochastic cost frontier approach. International Journal of Applied Econometrics and Quantitative Studies, 2(4), 19 - 36.
Kirti, and Shin, (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on Insurers. https://www.imf.org/~/media/Files/Publications/covid19-special-notes/en-special-series-on-covid-19-impact-of-covid-19-on-insurers.ashxf*
Nayak, Bhattacharyya, (2021). The Changing Narrative in the Health Insurance Industry: Wearables Technology in Health Insurance Products and Services for the COVID-19 World. Journal of Health Management 22(4) 550– 558, 2020 © 2021 Indian Institute of Health Management Research Reprints and permissions: in.sagepub.com/journals-permissions-india DOI: 10.1177/0972063420983112 journals.sagepub.com/home/jhm
Ross, Westerfield, Jordan, (2017). Essentials of Corporate Finance, 9th edition, McGraw-Hill Education.
Taylor, (2020). The Spanish Flu and the Stock Market: The Pandemic of 1919 https://www.globaltrademag.com/the-spanish-flu-and-the-stock-market-the-pandemic-of-1919/*
Farooq, Nasir, Bilal & Quddoos (2021) The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on abnormal returns of insurance firms: a cross-country evidence, Applied Economics, 53:31, 3658-3678, DOI: 10.1080/00036846.2021.1884839
Wang, Donghao Zhang, Xiaoquan Wang & Qiuyao Fu (2020) How Does COVID-19 Affect China’s Insurance Market? Emerging Markets Finance and Trade, 56:10, 2350-2362, DOI: 10.1080/1540496X.2020.1791074
